Introduction
Welcome to this module on entrepreneurship in the digital era. In this course, you will explore how everyday problems can become opportunities for action and learning. Entrepreneurship is not only about starting a business or using advanced technology, it’s about creativity, problem-solving and making smart choices with the tools you already have.
You will learn through real examples, short activities, and reflection. Take your time, stay curious and remember – small ideas and small steps can lead to meaningful change.
Let’s begin.
Learning outcomes
- Entrepreneurship basics (H)
- Digital tools in business (H)
- Creativity and innovation
- Business risks (H)
- Collaboration principles
- Problem-solving
- Using digital tools (H)
- Creative thinking (H)
- Testing ideas (H)
- Teamwork
- Willingness to learn (H)
- Risk awareness (H)
- Self-confidence (H)
- Ethical mindset
- Persistence
1. Developing a Business Idea and the Possibilities to Implement it
Evaluating a Business Idea and Its Viability
Content and Tasks:
- Developing a business idea
- SWOT Analysis: Assessing risks and opportunities (Internal and external factors)
- Business Model Canvas (BMC)
- Information sources that support starting a business
- Assessing the business idea and the possibilities to implement it
The student
- generates a business idea considering customers’ needs
- finds key services and information sources that support setting up a business
- determines the networks required to realize the business idea
- assesses the financial preconditions for implementing the business idea
- assesses their capacities for working as an entrepreneur
- determine the risks and opportunities involved in business

2. Business Idea
A business idea expresses the core purpose of the business. It answers these key questions: what, why, to whom, and how.
What makes a business idea viable? Search for information about business ideas, using several internet sources. Generate a business idea for a business that is under planning, imaginary, or maybe already existing.
Your approach should be customer-centered and cost-efficient, also taking into consideration the current business environment.
To create a business idea, follow these key steps:
- Identify a Need or Problem: Look for needs or issues not met in your community or industry that you can address.
- Innovate: Develop a unique solution or improve an existing product or service.
- Evaluate Feasibility: Is the idea practical and profitable? Do you have the resources, skills, and market demand?
- Market Research: Understand your target market, competition, and trends.
- Revenue Model: Plan how your business will make money.
These steps provide a foundation for developing a solid business idea.
3. SWOT analysis
To succeed as an entrepreneur, you must be prepared to take calculated risks. Business risks can be e.g. financial risks, information security risks, contractual risks, liability risks, business interruption risks or environmental risks. You can partially prepare for risks with insurance.
A SWOT analysis is a strategic tool for evaluating and understanding some essential internal and external factors in a business, your experience, knowledge, and strengths. SWOT analysis allows you to map the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of a business idea, entrepreneur, and company. This technique can also be used at the business ideation stage and will help you understand if you should introduce a new product or service. The following image will give you an overview of SWOT.
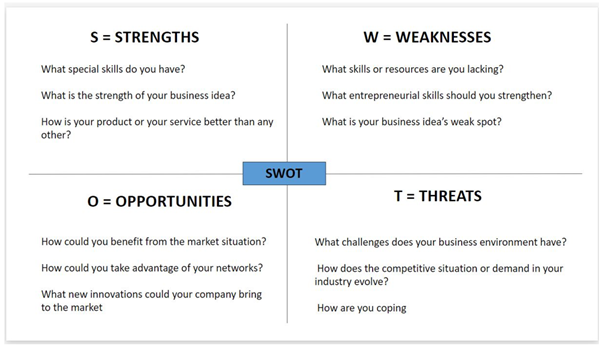
Task:
Document all essential strengths and weaknesses, opportunities, and threats on your business idea that you might already have or could possibly have in mind.
Optional task:
After filling done, reflect on all fields shortly, how to maintain strengths and utilize them better, how to improve weaknesses at least on basic level, what opportunities could bring on and how to make them possible, and finally, how to prepare for threats and what plans should be ready upon realization.
4. Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas is a visual representation of the 9 key building blocks that form the foundations of every successful business. It’s a visual overview of your entire business on a single canvas containing these 9 key building blocks:
Customer Segments
Value Propositions
Channels
Customer Relationships
Revenue Streams
Key Resources
Key Activities
Key Partners
Cost
An example of Business Model Canvas: Zara. Note that the example provided is very basic and that your canvases should be more detailed. (See instructions for each part of the canvas below.)
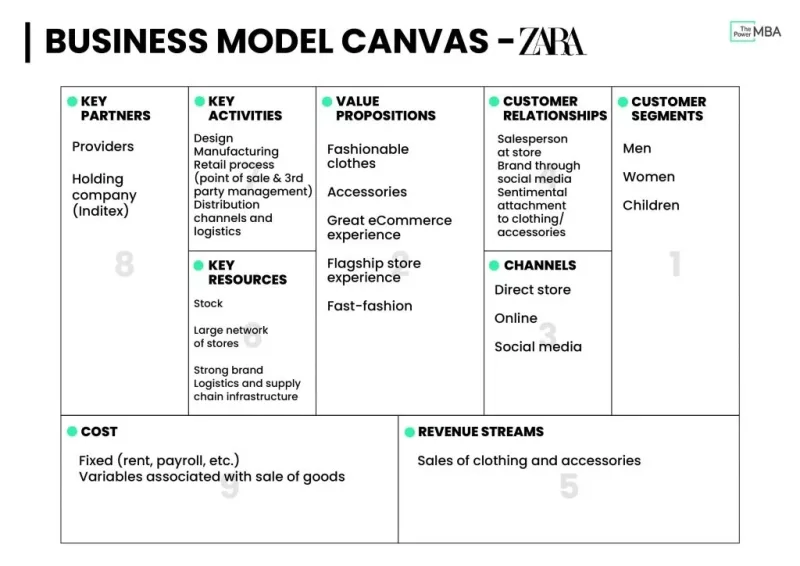
Source: The 9-Step Business Model Canvas Explained (http://thepower.education)
5. Explanations of business model canvas “ingredients”
Case study
Case study 1

Case study 2

Activity 1: Digital Tools in Everyday Life
Digital technology is not only computers and the internet. In everyday life, digital tools include mobile phones, SMS, mobile money, radios, and simple apps.
In many Sub-Saharan African communities:
- People use mobile money instead of banks
- Small businesses advertise through WhatsApp or Facebook
- Farmers receive weather or price information by SMS
These tools already support work, income, and learning, even without advanced devices. Digital entrepreneurship starts by recognising what tools people already use, not by buying expensive technology.
Self-directed task: Sort & reflect
Activity 2: Planning Your Own Learning & Skill Growth
Vocational learning is not only about school. Skills grow through:
- Daily practice
- Community learning
- Informal work
- Problem – solving
Digital skills include:
- Communication
- Organisation
- Basic data tracking
- Online safety
These skills are important for future jobs and self-employment.
Self-directed task: Match & Plan
Activity 3: Creativity – Turning Everyday Problems into Ideas
Key concept: Creativity is problem-solving
Creativity is not only art or design. In vocational life, creativity means finding new ways to solve familiar problems.
In many communities: Water collection takes time, Transport is unreliable, Information spreads slowly, young people have skills but few opportunities
Creative thinking begins by observing daily challenges and asking:
“What small change could make this easier?”
Digital entrepreneurship often starts with simple ideas, not complex technology.
Self-directed task: Problem -Idea
Summary of Key Learning Points
-
Entrepreneurship is about solving real-life problems and creating value, not only about starting a business.
-
Small experiments and smart risk-taking help entrepreneurs learn and reduce uncertainty.
-
Creativity means finding new and practical ways to improve familiar situations.
-
Digital entrepreneurship can begin with simple, everyday tools such as mobile phones, messaging apps and mobile money.
-
Collaboration and sharing ideas with others strengthen learning and business outcomes.
You have now built essential knowledge about entrepreneurship and digital tools, developed practical skills for problem-solving and collaboration and strengthened key attitudes such as confidence, responsibility, and persistence.
Entrepreneurship grows through creativity (seeing problems differently), innovation (trying new ideas) and smart risk-taking (testing small actions and learning from the results). You do not need perfect conditions or advanced technology to begin.
Take what you have learned and apply it in your own context. Choose one idea, use one familiar tool and take one small step forward. Learning continues through action.


